A block is hanging from a massless cord – A block hanging from a massless cord is a fundamental system in physics that demonstrates the interplay of forces, motion, and energy. This article delves into the intricacies of this system, exploring its components, forces, equations of motion, energy considerations, and real-world applications.
The block-cord system is a simplified model that allows us to isolate and study the essential principles governing the motion of objects under the influence of gravity and tension.
Define and Describe the System
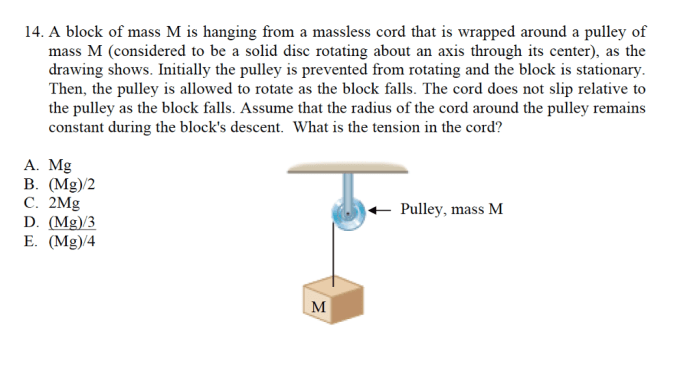
A block hanging from a massless cord is a simple mechanical system that consists of a block attached to a cord that is suspended from a fixed point. The block is typically assumed to be rigid and of uniform density, while the cord is assumed to be inextensible and massless.
The components involved in the system include:
- Block: The block is the object that is suspended from the cord. It is typically made of a material such as wood, metal, or plastic.
- Cord: The cord is the flexible material that connects the block to the fixed point. It is typically made of a material such as nylon, cotton, or wire.
- Fixed point: The fixed point is the point from which the cord is suspended. It is typically assumed to be stationary.
Forces Acting on the System: A Block Is Hanging From A Massless Cord
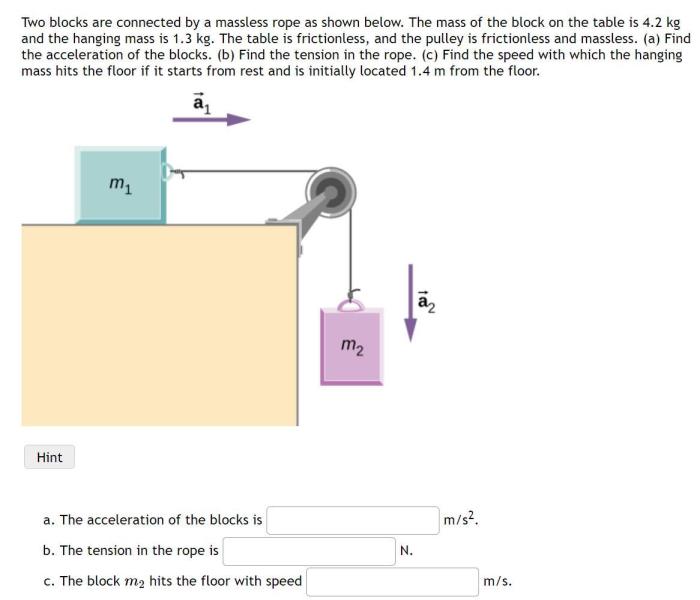
The forces acting on the block hanging from a massless cord include:
- Gravity: Gravity is the force that pulls the block downward. The magnitude of the gravitational force is given by Fg= mg , where mis the mass of the block and gis the acceleration due to gravity.
- Tension: Tension is the force that the cord exerts on the block. The magnitude of the tension force is equal to the weight of the block, which is FT= mg .
These forces interact and affect the motion of the block as follows:
- Gravity pulls the block downward, causing it to accelerate downward.
- Tension opposes the force of gravity, preventing the block from falling.
Equations of Motion
The equations of motion that govern the movement of the block hanging from a massless cord are:
- Fnet= ma , where Fnetis the net force acting on the block, mis the mass of the block, and ais the acceleration of the block.
- Fg– F T= ma , where Fgis the force of gravity, FTis the tension force, and ais the acceleration of the block.
These equations can be used to analyze the motion of the block and to determine its velocity, acceleration, and position at any given time.
Energy Considerations
The energy transformations that occur within the block-cord system include:
- Gravitational potential energy: The block has gravitational potential energy due to its position above the ground. The gravitational potential energy is given by Ug= mgh , where mis the mass of the block, gis the acceleration due to gravity, and his the height of the block above the ground.
- Kinetic energy: The block has kinetic energy due to its motion. The kinetic energy is given by K = (1/2)mv2, where mis the mass of the block and vis its velocity.
The conservation of energy principle states that the total energy of the block-cord system remains constant. This means that the gravitational potential energy lost by the block as it falls is converted into kinetic energy.
Applications and Examples
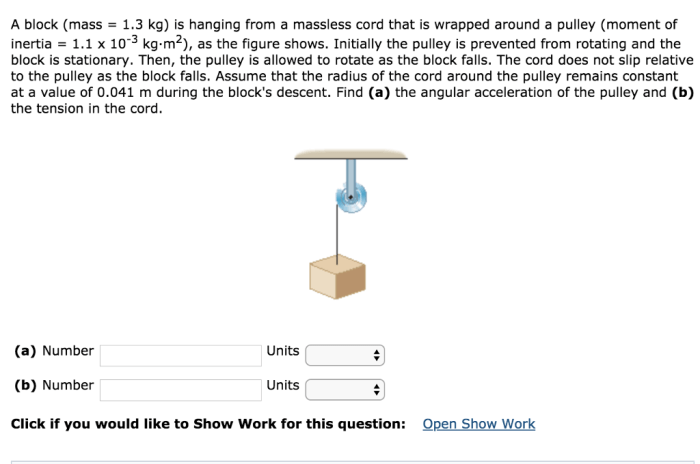
The concept of a block hanging from a massless cord is applicable to a wide variety of real-world situations, including:
- Pendulums: A pendulum is a weight suspended from a cord or chain that swings back and forth. The period of a pendulum is determined by the length of the cord and the acceleration due to gravity.
- Elevators: Elevators use a system of pulleys and cables to lift and lower a platform. The weight of the platform and its contents is balanced by a counterweight, which is suspended from a cord that passes over a pulley.
- Cranes: Cranes use a system of pulleys and cables to lift and move heavy objects. The weight of the object being lifted is balanced by a counterweight, which is suspended from a cord that passes over a pulley.
The principles learned from studying the block-cord system can be extended to more complex systems, such as those involving multiple masses, pulleys, and friction.
Essential FAQs
What is the tension in the cord?
The tension in the cord is equal to the weight of the block, mg.
What is the acceleration of the block?
The acceleration of the block is g, the acceleration due to gravity.
What is the energy of the block?
The energy of the block is equal to its potential energy, mgh, where h is the height of the block above the ground.