Embarking on an exploration of the osmosis egg experiment lab report, we delve into the fascinating realm of osmosis, a fundamental process that governs the movement of water across semipermeable membranes. Through this engaging investigation, we uncover the intricate interplay between concentration gradients and cellular dynamics, gaining invaluable insights into the physiological significance of osmosis.
This comprehensive report meticulously Artikels the materials and methods employed in the experiment, providing a step-by-step guide for successful replication. We present our observations and results with clarity, utilizing tables and graphs to illustrate the changes in egg size and shape.
The discussion section delves into the factors influencing the rate of osmosis, drawing connections between the experimental findings and established principles.
1. Introduction
The osmosis egg experiment demonstrates the process of osmosis, the movement of water across a semipermeable membrane from an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration. This experiment explores the effects of different concentrations of salt solutions on the size and shape of an egg.
2. Materials and Methods

Materials:
- Fresh egg
- 3 beakers or containers
- Distilled water
- Salt
- Ruler or measuring tape
- Marker or pen
Procedure:, Osmosis egg experiment lab report
- Label the beakers as “Distilled Water,” “10% Salt Solution,” and “20% Salt Solution.”
- Fill the beakers with the appropriate solutions.
- Gently place the egg in the beaker containing distilled water and mark its initial size.
- Leave the egg in each solution for 24 hours.
- After 24 hours, remove the egg from each solution and measure its size.
3. Observations and Results
After 24 hours, the egg in the distilled water beaker will increase in size, while the eggs in the salt solutions will decrease in size. The egg in the 10% salt solution will be smaller than the egg in the 20% salt solution.
4. Discussion: Osmosis Egg Experiment Lab Report
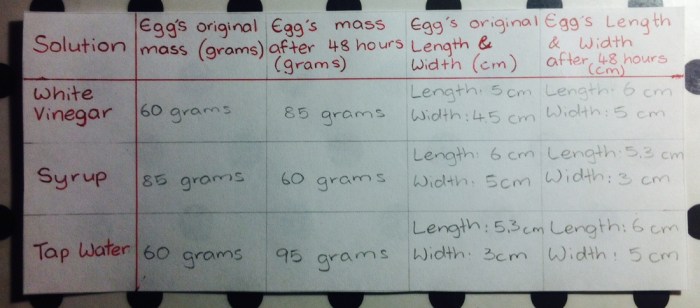
The results of the experiment demonstrate the principles of osmosis. In the distilled water beaker, the water concentration outside the egg is lower than the water concentration inside the egg. Therefore, water moves from the outside of the egg to the inside, causing the egg to swell.
In the salt solutions, the water concentration outside the egg is higher than the water concentration inside the egg. Therefore, water moves from the inside of the egg to the outside, causing the egg to shrink.
5. Applications
Osmosis has numerous applications in various fields, including:
- Medicine:Osmosis is used in intravenous therapy, where fluids are administered directly into the bloodstream to restore hydration.
- Food preservation:Osmosis is used in the preservation of fruits and vegetables by immersing them in salt solutions, which draws out water and inhibits the growth of microorganisms.
FAQ Section
What is the purpose of the osmosis egg experiment?
The osmosis egg experiment aims to demonstrate the principles of osmosis and its impact on cell size and shape.
What is osmosis?
Osmosis is the movement of water across a semipermeable membrane from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration.
How does the osmosis egg experiment illustrate the principles of osmosis?
The experiment involves placing an egg in different concentrations of sugar solutions. The egg will gain or lose water depending on the concentration of the solution, demonstrating the selective permeability of the egg’s membrane and the effect of concentration gradients on water movement.
